Weak passwords are highly susceptible to brute-force attacks, and while strong passwords offer a better defense, they are not entirely invulnerable. To significantly enhance the security of your account, it is highly recommended to implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for logging in. Passwords serve as the initial layer of defense; MFA introduces a crucial second security layer to your authentication process. Currently, this secondary layer typically involves one-time passwords, often referred to as verification codes, which are generated by a dedicated MFA application on your smartphone. Throughout this guide, we will refer to these as verification codes.
Configuring Multi-Factor Authentication with Verification Codes
- Begin by installing a multi-factor authentication application on your smartphone. Popular options include Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, or any other compatible MFA app you prefer.
- Navigate to your account's My Profile section. Scroll down until you locate the “Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)” segment, then proceed by clicking the provided link.
- Check the box labeled “Enable Multi-factor Authentication” to activate the feature.
- Using your smartphone, scan the QR code displayed on your screen. Upon successful scanning, your chosen authentication app will show the hostname of your server. Applications like Google Authenticator typically display a 6-digit verification code directly beneath the hostname. For other MFA apps, you might need to tap on the hostname to reveal the code.
- Input the verification code generated by your MFA app into the designated field.
- To avoid entering a verification code every time you log in, you can select the “Enable the “Remember Device” feature” checkbox. Important Warning: This feature should only be enabled on devices that are exclusively yours and secure. Enabling it on a shared or public device could potentially allow unauthorized access to your account.
- When the “Remember Device” feature is active, you will not need to provide a verification code for logins from that specific device for a predetermined number of days. After this period expires, or if your browser's cache is cleared, you will be prompted to enter a verification code once more.
- With the “Remember Device” feature enabled, your browser will retain your device's recognition for the duration you specified. However, accessing your account from a new or different device will always require a verification code. On these new devices, you will also see a checkbox labeled “Remember this device for N days,” where 'N' corresponds to the number of days you previously configured. To ensure this “Remember Device” checkbox is automatically selected by default whenever you log in from an unfamiliar device, enable the “Preselect the “Remember Device” checkbox” option.
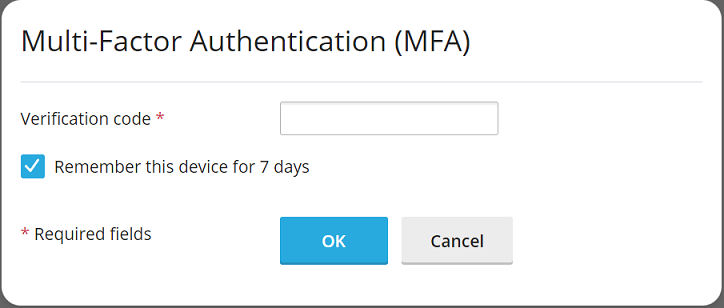
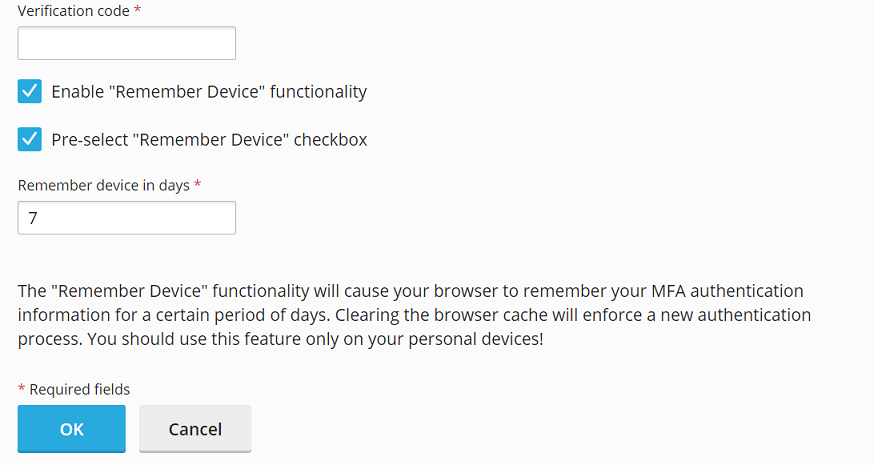
- Finalize the setup by clicking OK.
Congratulations, Multi-Factor Authentication is now successfully configured for your account. From this point forward, logging in will require you to enter a verification code generated by your MFA application to ensure heightened security.
Enforcing Multi-Factor Authentication Across Accounts
The platform facilitates MFA through a dedicated Multi-Factor Authentication extension, which is typically installed by default. Once this extension is active, any account owner can configure MFA for their individual account. For environments requiring even stricter security, administrators may choose to enforce MFA usage across all accounts, either with or without an option for users to bypass the setup. If enforcement is strict, users will be unable to log in without first configuring MFA.
Important Note: It is crucial to understand that there is currently no selective enforcement option for MFA; it cannot be applied to only certain accounts or account types. The following instructions will enforce MFA universally for all accounts, including administrative accounts.
Steps to Enforce MFA
- First, ensure that MFA has been set up for your administrator account using the procedure outlined in the previous section.
- Locate and open the
panel.iniconfiguration file for editing. Its typical locations are:- For Linux installations:
/usr/local/psa/admin/conf/panel.ini - For Windows installations:
%plesk_dir%admin\conf\panel.ini
Panel.inieditor extension is available. - For Linux installations:
- Based on your desired enforcement policy, add one of the following configurations to the
panel.inifile and then save your changes:Strict Enforcement (No Bypass):
To mandate MFA without allowing users to bypass the setup, include these lines:
[ext-mfa] enforce = true allowSkipEnforce = falseWith this setting, any user attempting to log in without MFA configured will be presented with a message indicating that they cannot proceed until MFA is properly set up.

Flexible Enforcement (Bypass Allowed):
To enforce MFA while still providing users the option to bypass the initial setup, add these lines:
[ext-mfa] enforce = true allowSkipEnforce = trueIn this scenario, users logging in without MFA will see a similar message, but they will have the choice to skip the MFA setup and continue using the platform. However, this reminder will reappear with every subsequent login until MFA is eventually configured.

- (Optional) After MFA enforcement is active, users will encounter one of the aforementioned messages, which may include a link to a knowledge base article explaining the benefits and functionality of MFA. Should you wish to direct users to an alternative informational resource about MFA, you can customize this link. To do so, add the following lines to the
panel.inifile and save:[ext-mfa] learnMoreUrl = https://example.com ; Replace https://example.com with the URL of your preferred web page.




