Deploying Odoo 16 with Docker on Plesk: Addressing Common Installation Hurdles
Deploying Odoo 16 within a Dockerized environment on a Plesk server can sometimes present unique challenges. Users often encounter difficulties during the initial setup and configuration, leading to perplexing errors that hinder a smooth deployment. This article delves into the common obstacles faced by users attempting to run Odoo 16 via Docker on Plesk, providing insights and best practices to overcome them.
Understanding Initial Deployment Obstacles
A frequent point of concern for users involves the initial stages of Docker container deployment for Odoo. The process can seem to stall, leaving administrators unsure of the next steps or whether the application is progressing as expected. One specific area that often requires careful attention is volume allocation, which dictates how data is persisted and accessed by the Docker containers.
During deployment, issues related to volume mounting can arise. An "address not mounted" error indicates that the Docker container is unable to access the specified host path for data storage, which is crucial for Odoo's operation. This can lead to subsequent failures as the application cannot properly initialize or store its data.

Another common scenario involves the automatic filling of volume paths when they are initially left blank. While this might seem convenient, it's essential to ensure these automatically generated paths are correctly configured and accessible to prevent issues down the line.
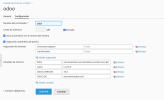
Database Connection Difficulties
Perhaps one of the most significant hurdles is encountering database errors. Despite PostgreSQL (the database system Odoo relies on) appearing to run flawlessly, the Odoo container might still report connection failures. This often manifests as an inability to establish a connection to port 5432, which is the default port for PostgreSQL. Such errors can be particularly frustrating when the database service itself shows no signs of malfunction.
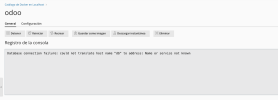
Verifying that the PostgreSQL service is active and running is a crucial first step in troubleshooting, as shown in diagnostic outputs.
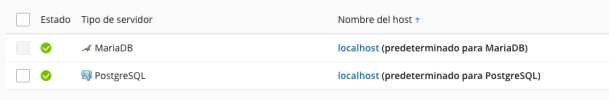
The Critical Role of PostgreSQL Container Configuration
The root cause of many database connection issues when deploying Odoo via Docker on Plesk lies in the isolation of Docker containers. An Odoo container does not inherently connect to a PostgreSQL service running on the host or even another unrelated Docker container without explicit configuration. For a successful Odoo deployment, it is imperative to set up a dedicated PostgreSQL container and ensure the Odoo container is correctly linked to it.
This means that instead of relying on a standalone PostgreSQL installation or a generic database service, a separate Docker container specifically running PostgreSQL must be provisioned. The Odoo Docker container then needs to be configured to communicate with this specific PostgreSQL container. This typically involves using Docker's networking features, such as defining a custom network and linking the containers, or using environment variables within the Odoo container to point to the PostgreSQL container's hostname and port.
A common error message like "could not establish the connection with port 5432 of Postgres" is a direct indicator that this inter-container communication is not correctly established. Even if PostgreSQL is running, if the Odoo container cannot find or access it on the specified port within its network context, the connection will fail.
Best Practices for a Seamless Odoo Docker Deployment on Plesk
To mitigate these challenges and ensure a robust Odoo 16 deployment on Plesk using Docker, consider the following best practices:
- Dedicated Database Container: Always run PostgreSQL in its own dedicated Docker container. This promotes isolation and easier management.
- Container Networking: Utilize Docker's networking capabilities to link the Odoo and PostgreSQL containers. This allows them to communicate securely and efficiently.
- Volume Management: Carefully plan and configure Docker volumes for both Odoo and PostgreSQL to ensure data persistence and prevent "address not mounted" errors. Explicitly define host paths for volumes rather than relying on automatic allocation.
- Environment Variables: Configure the Odoo Docker container with the necessary environment variables to specify the database host, port, username, and password, ensuring it can correctly connect to the PostgreSQL container.
- Firewall Configuration: Ensure that the Plesk firewall or any other server-level firewall allows traffic between the Docker containers on the necessary ports (e.g., 5432 for PostgreSQL).
- Review Logs: Regularly check the Docker logs for both Odoo and PostgreSQL containers. These logs provide invaluable information for diagnosing connection issues, configuration errors, and other deployment problems.
By carefully addressing these common pitfalls and adhering to best practices for Docker container management and networking, you can achieve a stable and functional Odoo 16 installation on your Plesk server.




