Data loss can be a significant setback for any website or server administrator. Implementing a robust backup strategy is crucial for safeguarding your digital assets. Plesk Obsidian offers advanced backup solutions, including the highly efficient incremental backup method, designed to optimize resource usage while ensuring your data remains secure and recoverable.
What is an Incremental Backup?
Plesk provides two primary types of backup strategies to protect your valuable data:
- Full Backup: Each time a full backup is performed, it captures all data, irrespective of when it was last updated. This provides a complete snapshot of your system at that specific moment.
- Incremental Backup: In contrast, an incremental backup is a more resource-efficient option, storing only the data that has undergone changes since the previous backup, whether that was a full or another incremental backup.
The strategic use of incremental backups offers several distinct advantages. It significantly reduces the time required for backup operations, minimizes the load on your server's CPU, and conserves valuable disk space, thereby enhancing overall backup performance and efficiency. This method is particularly beneficial for frequently updated websites or applications where a full backup might be overly burdensome.
When performing an incremental backup, Plesk intelligently includes the following data:
- Web hosting data that has been modified since the last backup (which could be either a full or a previous incremental backup).
- Mail data that has been altered since the last backup (again, either a full or a previous incremental backup).
- A complete full backup of all database data.
It's important to note that incremental backups in Plesk capture entire files that have been created or modified within a subscription, rather than just parts of them. Plesk utilizes an internal mechanism, an index file, to determine which files have changed. This index file is generated with each backup and meticulously lists all files present in a subscription, along with critical information such as their size, last modification date, permissions, and owner. A full backup's index file will list all existing files, while an incremental backup's index will only contain information for the files that have changed.
Plesk employs a precise set of criteria to ascertain whether a file should be included in an incremental backup:
- If the file was not present in the index of previous backups (both full and incremental).
- If the file’s size or its last modification timestamp differs from the records in the index of the previous backup.
- If there have been changes to the file’s permissions or its designated owner.
How to Create an Incremental Backup
Creating a backup in Plesk is a straightforward process. Navigate to the Backup Manager page, which can be accessed from the server, user account, or subscription level, depending on your needs. On this page, click the Back Up button. You will then be presented with the option to choose between a Full or an Incremental backup.
It is crucial to understand that the very first backup you perform will always be a full backup, regardless of your selected type. Subsequent backups, if chosen as Incremental, will then only save the web hosting and mail data that has changed since that initial full backup. This results in an efficient backup chain comprising a foundational full backup followed by a series of incremental backups, each capturing only the latest changes.
On the Backup Manager page, incremental backups are easily identifiable by their 'Incremental' label, allowing you to quickly distinguish them from full backups.
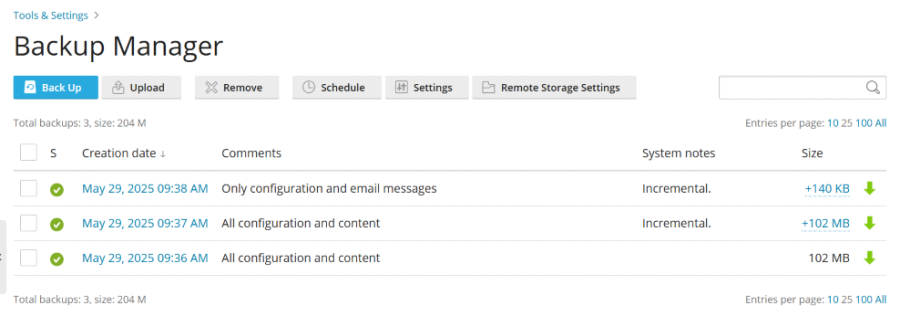
Note: Maintaining the integrity of your backup chain is vital. If any incremental backup within a sequence becomes lost or corrupted, all subsequent incremental backups in that chain will be marked with a yellow exclamation mark icon. Attempting to restore from such a compromised chain will trigger a warning message, informing you about the missing incremental backups. Furthermore, be aware that removing an incremental backup will lead to the automatic removal of all subsequent backups in that particular chain.
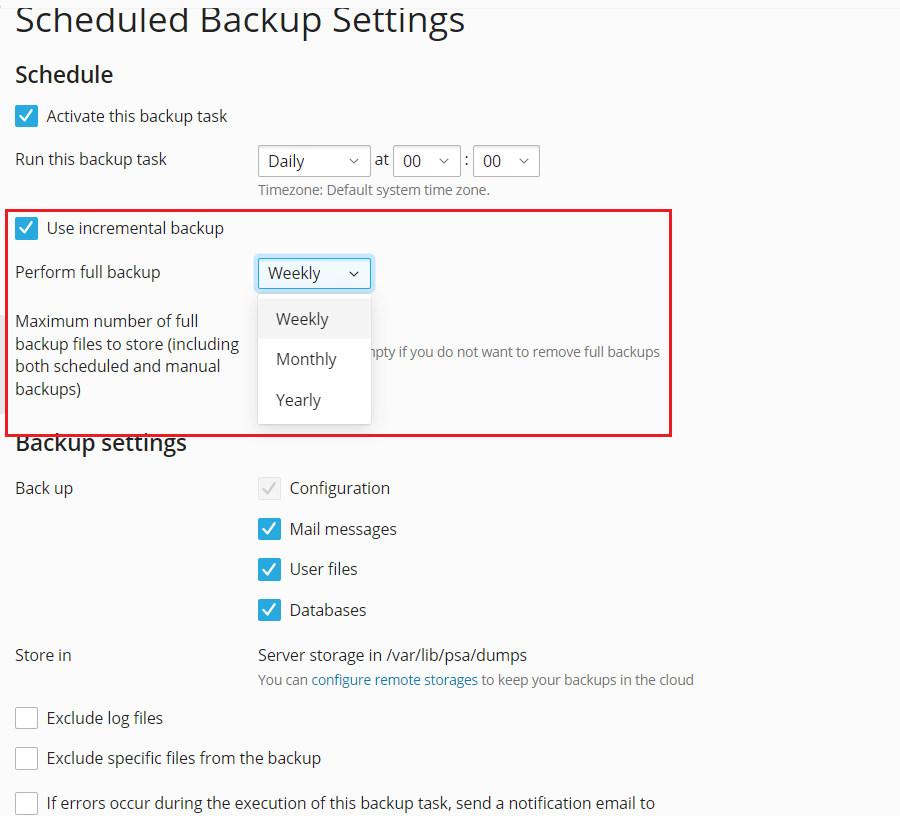
While incremental backups are highly efficient, it is a recommended best practice to perform a full backup of your data periodically. The frequency of these full backups (e.g., weekly or monthly) should align with how often your web content or mail data is updated. If you utilize scheduled backups within Plesk and activate the Use incremental backup option, you will also be prompted to specify a period for executing full backups, ensuring a balanced and robust backup strategy.
Note: Enabling the Use incremental backup option for scheduled backups does not override or disable your periodic full backups. Both scheduled backup types operate independently on their own predefined intervals, offering comprehensive data protection.
How to Restore an Incremental Backup
When the need arises to restore data using an incremental backup, Plesk intelligently reconstructs your environment. The restoration process involves seamlessly integrating all unchanged data from your most recent full backup with the accumulated changes from all subsequent incremental backups created after that full backup. This comprehensive approach ensures that your system is restored to the exact state it was in at the time the selected incremental backup was made.
Despite the complexity of reassembling data from multiple backup points, the restoration performance typically shows no noticeable degradation compared to restoring from a single full backup. Plesk efficiently manages the data integration, providing a smooth and timely recovery.
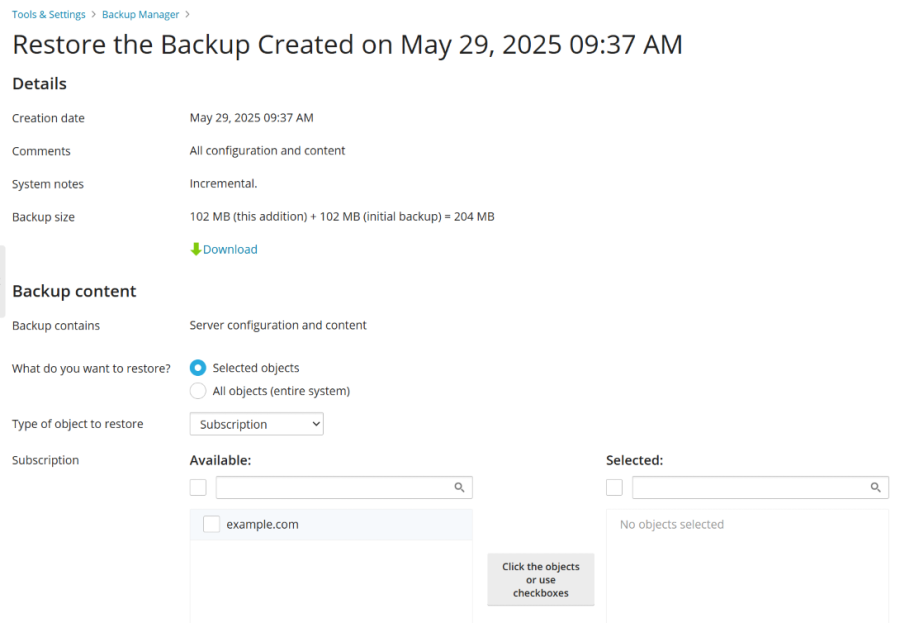
The Restore the Backup dialog offers a clear overview of all the constituent backups involved in the restoration. It displays the specific incremental backup you've selected, the cumulative data from all preceding incremental backups, and the initial full backup that forms the base of the chain. For maximum flexibility, you are also provided with options to download all these individual backup files if needed.