Are you spending valuable hours on tedious and repetitive server administration tasks? If so, mastering cron jobs can significantly streamline your workflow. This comprehensive article explores how cron, integrated with cPanel & WHM, empowers you to automate these essential yet time-consuming aspects of web hosting management.
Cron is a powerful, time-based job scheduler. It enables server administrators to automatically execute scripts, known as cron jobs, at pre-defined intervals. While cPanel & WHM already utilizes cron for various critical server maintenance scripts, you and your users also have the flexibility to schedule your own custom scripts. For instance, you could configure a personalized backup script to run precisely at 7 a.m. every morning, ensuring your data is always secure and up-to-date.
In this guide, we will delve into the common applications of cron, demonstrate how to effectively schedule scripts, and walk through the process of adding new jobs to effortlessly automate your server administration responsibilities.
Understanding the Typical Uses of a Cron Job
Cron is remarkably versatile, capable of executing simple commands, complex shell scripts, and programs developed in popular languages like PHP, Python, and Perl. Essentially, if a task can be initiated from the command line or through a script, it can be efficiently automated using this robust task scheduler.
Common Cron Job Use-Cases Include:
- Log Rotation: Automate the archiving of old log files at specified intervals to prevent them from growing to unmanageable sizes, ensuring optimal disk space and performance.
- User Notifications: Schedule alerts to inform users when they are nearing their allocated resource limits, promoting proactive management.
- Automated Updates: Configure regular checks for security updates and automatically apply them, maintaining a secure and up-to-date server environment without manual intervention.
- Content Management System (CMS) and Database Backups: Guarantee that crucial backups for your websites and databases are completed consistently, eliminating the risk of data loss due to human oversight.
Configuring a Cron Job in cPanel: Mastering the Notation
Cron relies on a concise notation system to define execution times and days. A typical configuration line, often referred to as a "crontab entry," might appear as follows:
30 23 25 * * myscript.shThis format consists of five whitespace-separated fields that specify time intervals, immediately followed by the command or script to be executed. The schedule itself is stored within a "crontab" file, which is essentially a list of jobs along with their directives. While you can edit this file directly via SSH using the crontab command, cPanel & WHM offers a significantly faster and more user-friendly approach. It provides two dedicated interfaces for scheduling jobs: one for cPanel’s internal maintenance scripts and another for user-defined scripts, which we will explore in detail.
Before proceeding to cPanel's intuitive cron configuration interface, it's crucial to have a solid understanding of the interval notation. The time fields represent the following, from left to right:
- Minutes: A number ranging from 0 to 59.
- Hours: A number from 0 to 23. Cron utilizes a 24-hour clock format, meaning 4 p.m. is represented as 16, 11 p.m. as 23, and so forth.
- Days of the month: A number between 1 and 31.
- Months: A number from 1 to 12 (January to December).
- Days of the week: A number between 0 and 7, where both 0 and 7 typically represent Sunday.
Fields containing an asterisk (*) signify that the job will run at every possible interval compatible with the other specified fields. Reverting to our initial example of "30 23 25 * *", this translates to the 30th minute of the 23rd hour (11 p.m.) on the 25th day of the month. Because the Month and Day of Week fields contain asterisks, this script will execute at 11:30 p.m. on the 25th of every month, regardless of the specific day of the week or month.
Let's consider some more intricate examples to solidify your understanding. Imagine you have a monitoring script that needs to run hourly, precisely on the hour, between 9 a.m. and 5 p.m., but exclusively on weekdays. To achieve this, we introduce another powerful piece of notation: the range.
00 9-17 * * 1-5 myscript.shRanges are specified by values separated by a hyphen (-). This example breaks down as follows:
00: Specifies the first (or zeroeth) minute of the hour.9-17: Indicates each hour between 9 a.m. and 5 p.m. (inclusive).*: Denotes every day of the month.*: Denotes every month.1-5: Represents the days from Monday to Friday.
What if your requirement is slightly different? Instead of running every hour between 9 a.m. and 5 p.m., you want the script to execute at specific times: 9 a.m., 12 p.m., 3 p.m., and 6 p.m., still only on weekdays. For such discrete intervals, you’ll utilize one more notation element: the list.
00 9,12,15,18 * * 1-5 myscript.shThis example is similar to the previous one, but it employs a comma-separated list in the Hours field instead of a range. This allows for precise, non-consecutive time specifications.
The foundational concepts we've outlined here should effectively cover the vast majority of your cron scheduling needs. However, cron boasts an incredibly flexible notation system with additional shortcuts and advanced directives for highly specific scenarios. Should you wish to explore these advanced features further, we recommend you consult this informative article or examine the man page on your CentOS server by executing the command man 5 crontab in your terminal.
Configuring cPanel Cron Jobs within WHM
cPanel & WHM automatically schedules several critical system scripts, including the upcp update script, as well as the backup and cpbackup utilities. As a server administrator, you possess the control to fine-tune when these essential scripts are executed directly within WHM.
To access these settings, simply navigate to the sidebar menu and select Configure cPanel Cron Jobs, located under the Server Configuration section.
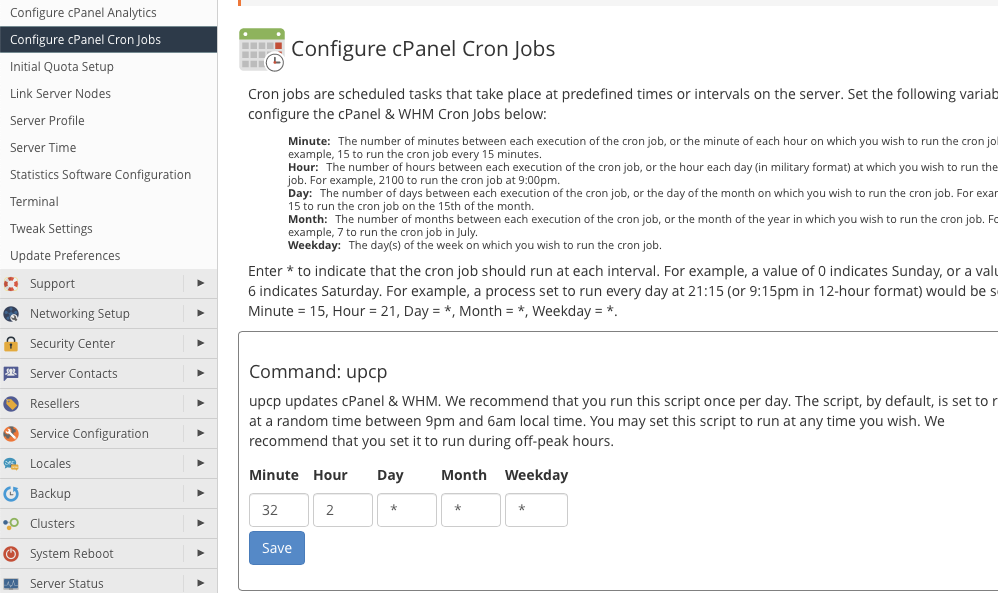
For each script listed, you will find five input fields designed for entering the cron notation we discussed earlier. While we provide sensible default settings, you have the complete freedom to adjust these to your preferred execution times, aligning with your server maintenance schedule.
Configuring Custom Cron Jobs in cPanel
For scheduling your own custom scripts, the process is straightforward within the cPanel interface. From the main page menu, locate the Advanced section and select Cron Jobs.
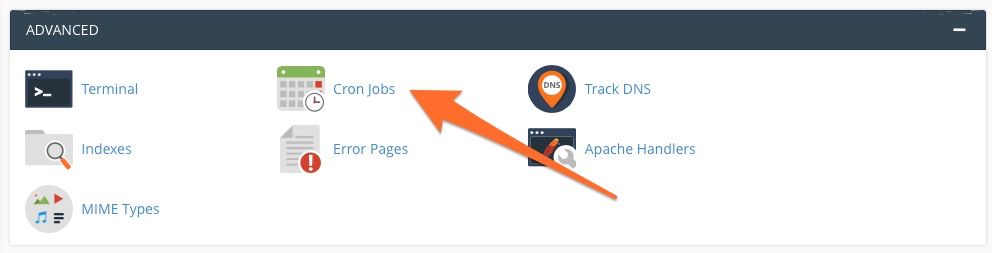
Upon entering the Cron Jobs interface, you will be presented with a dedicated table designed for adding new scripts and precisely defining their time intervals.
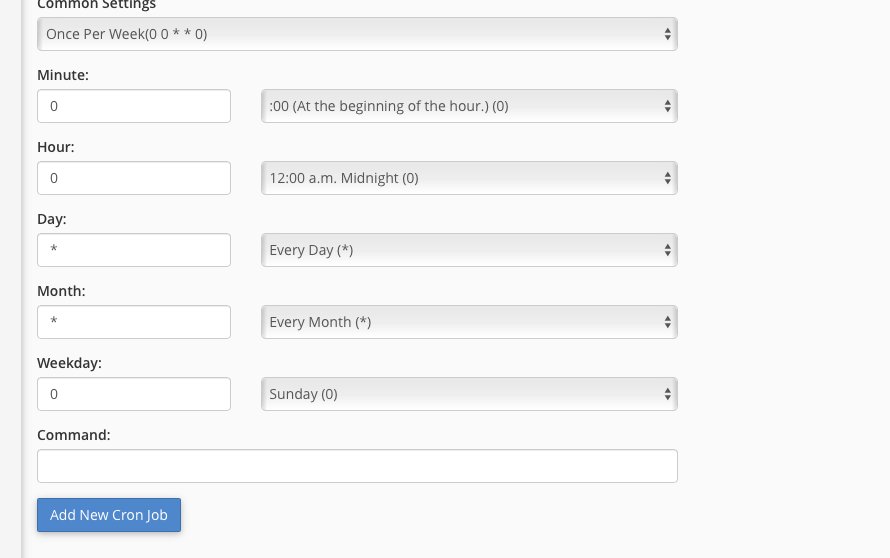
To further simplify the configuration process, we’ve included a convenient drop-down menu populated with common settings, such as "Once Per Week" or "Once Per Month." These pre-defined options can significantly speed up the setup for frequently used schedules.
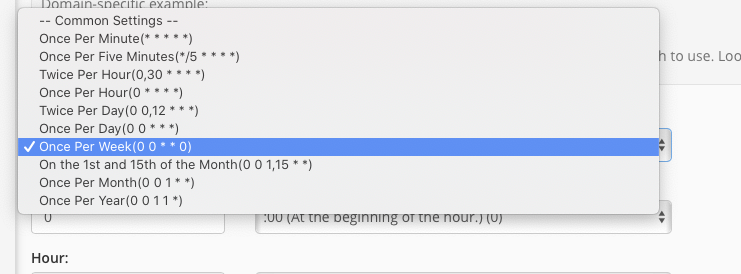
If the main drop-down menu doesn't offer a setting that precisely fits your requirements, you have two flexible alternatives. You can manually enter a custom time interval into the individual input boxes on the left, or utilize the discrete menus on the right to select from typical entries for each specific time period (minutes, hours, days, etc.).
Finally, enter the exact command or the full path to your script into the Command field. Once you’ve configured your desired schedule and command, click the "Add New Cron Job" button to save your entry. Cron will then automatically execute your script at the precise intervals you have selected, taking the repetitive task off your hands.
Conclusion
Cron is an incredibly simple yet profoundly powerful utility for automating a multitude of mundane, repetitive, and often easily forgotten server administration tasks. While the interval format may seem a little daunting at first glance, dedicating a few minutes to studying and understanding its logic will undoubtedly save you countless hours of manual work in the long run. When combined with the quick and user-friendly configuration tools available in cPanel and WHM, cron becomes an indispensable asset for efficient server management.
We are always eager to hear your thoughts and feedback. If you have any comments or questions regarding this article or anything else related to cPanel & WHM, please do not hesitate to let us know.




