Docker is a powerful platform designed for running applications within isolated environments known as containers. This technology allows you to deploy specific software, such as Redis or MongoDB, or even particular versions of software that may not be natively supported by your operating system or might require complex compilation processes.
Within Plesk, Docker is seamlessly integrated as an extension, providing a robust solution for managing and operating containers. This integration enables you to leverage various Docker images to run applications efficiently, whether on your local host server or across remote Docker environments.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the essential steps of creating, configuring, and effectively managing Docker containers directly within the Plesk interface. Additionally, you will learn how to extend your control to remote Docker hosts from your Plesk panel, enhancing your deployment capabilities.
Requirements and Limitations for Docker in Plesk
Important Security Notice: The Docker extension directly downloads images from Docker Hub without any pre-configuration. It is crucial to understand that some Docker containers and the software they contain are intended solely for trusted environments and may necessitate additional security measures. Before deploying any downloaded images in Plesk, you are responsible for enhancing their security. Always consult the documentation provided by the container or software vendor for specific security guidelines. For instance, refer to the security section in the Redis documentation for an example.
- Docker is officially supported in Plesk for the following operating systems: CentOS 7, Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7, Debian 10, Debian 11, Debian 12, Ubuntu 18.04, Ubuntu 20.04, Ubuntu 22.04, Ubuntu 24.04, AlmaLinux 8.x, AlmaLinux 9.x, Rocky Linux 8.x, and Virtuozzo 7 with Update 1 Hotfix 1 (7.0.1-686) or later. Please note that for Plesk on Windows, Docker must be installed on a remote machine. Refer to the "Using Remote Docker" section for more details.
- It is not possible to use Docker within a Plesk instance that is itself deployed inside a Docker container.
- Utilizing remote Docker services in Plesk requires an additional license. This can be acquired either separately or as part of a bundle such as the Hosting Pack, Power Pack, or Developer Pack.
- Docker functionality is exclusively available on x64 architectures.
- Direct migration or backup of Docker containers within Plesk is not supported. However, you can back up the data utilized by these containers (see "Volume Mapping" for more information) or download container snapshots.
- Virtuozzo 7 with Update 1 Hotfix 1 (7.0.1-686) or a later version is supported. It's important to be aware that with this update, new CentOS 7-based containers are created with the firewall enabled by default as part of Virtuozzo's enhanced security measures. Plesk administrators must manually configure the firewall to ensure all ports essential for Plesk operations are open.
Prerequisites for Docker Installation
Before you can begin leveraging Docker within your Plesk environment, the essential Docker extension must be installed on your Plesk server. Follow the appropriate instruction:
- If you possess Plesk administrator privileges, proceed to install the extension directly from the Extensions Catalog.
- If you are not the Plesk administrator, please reach out to your hosting provider and request them to install the Docker extension on your behalf.
Upon successful installation of the extension, you will be prepared to utilize Docker's capabilities. The "Docker" option will become visible and accessible within the Navigation Pane of your Plesk panel, indicating that the service is ready for use.
Managing Docker Containers in Plesk
Within Plesk, you can conveniently access a wide array of images from Docker Hub through the Run Container catalog. Navigate to Docker > Containers > Run Container to get started.
To open the catalog and browse available images:
- If you have not previously deployed any containers, click the Run Container button within Docker > Containers.
- If containers have been previously installed, click the plus icon
 in Docker > Containers.
in Docker > Containers.
Utilize the search box to easily find specific images. You can search by image name, repository, or a combination of both.
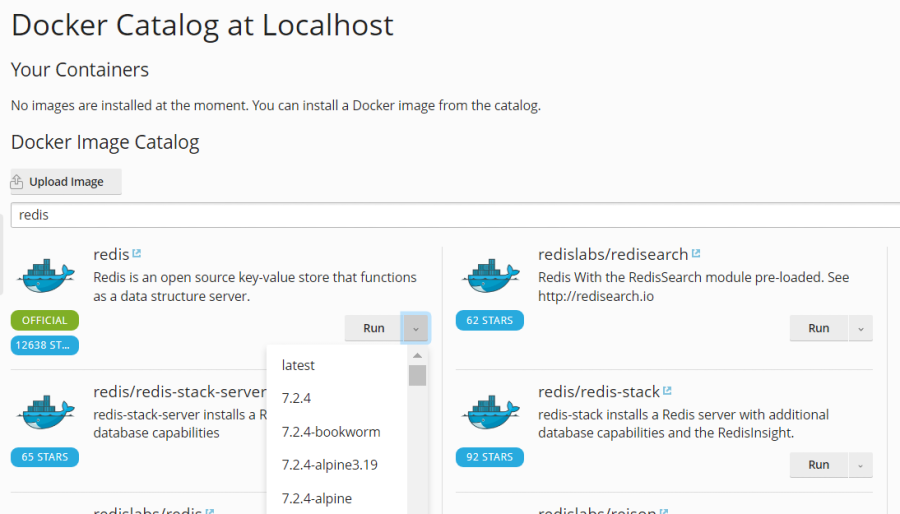
The search functionality covers two main repository types:
- Local repository: This contains images that have already been downloaded and are stored on your server, ready for immediate deployment. For more detailed information, refer to the "Managing Local Images" section of this guide.
- Docker Hub: The official public registry for Docker images, offering a vast collection of applications and services.
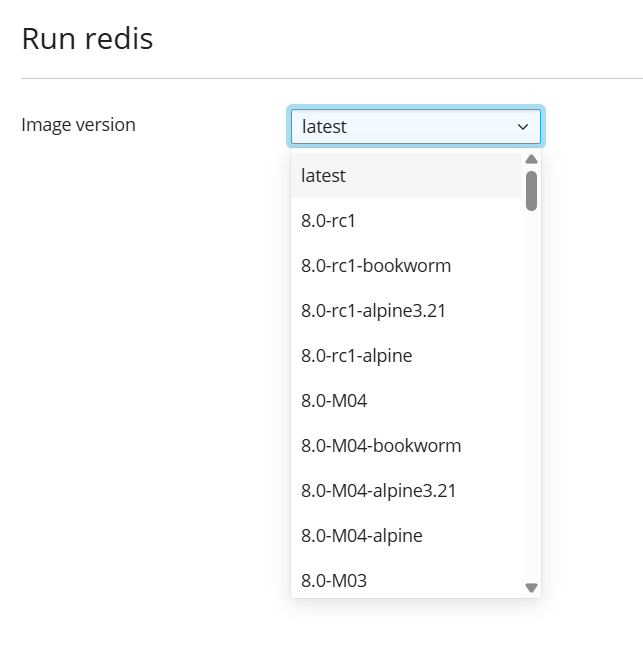
Many applications offer multiple versions. You can deploy a specific version by selecting the appropriate tag from the available options, as demonstrated below:
Follow these steps to run a new container:
- Navigate to Docker > Containers > Run Container.
- Use the search box to locate desired images within the catalog. Locally stored images will be indicated by (local) next to their version.
- For images from Docker Hub, click the more info icon
 to view its description and documentation on Docker Hub. This option is not applicable to local images.
to view its description and documentation on Docker Hub. This option is not applicable to local images. - Select the desired image card.
- To run a specific version, choose the preferred image version from the Image version drop-down menu, then click Next.
- To deploy the latest available version of the selected application, simply click Next.
Plesk will then initiate the container creation process and prompt you to configure its settings, including environment variables. You can halt this process at any time by clicking Cancel on the Settings screen. Comprehensive details regarding these settings can be found in the "Container Settings" section later in this document.
- After customizing your settings as needed, click Run. The newly created and running container will then appear in the list within the Containers tab.
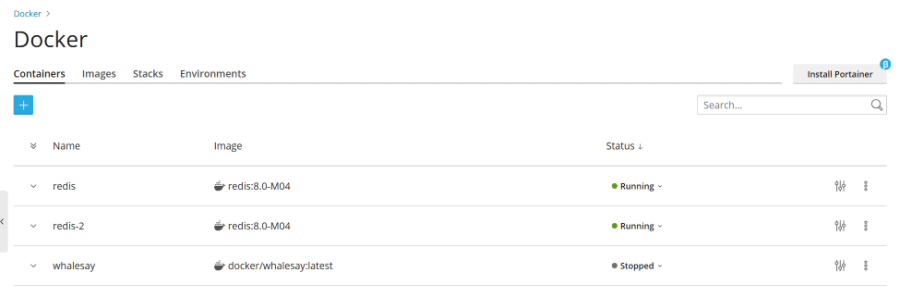
Always review the Console Log to confirm that the container is operating without any issues after deployment.
Configuring Docker Container Settings
Note: You do not need to stop a container to modify its settings. When you save new configurations, Plesk intelligently recreates the container to apply your changes.
To access and edit container settings, navigate to the Containers tab and click the settings icon ![]() adjacent to the container you wish to configure.
adjacent to the container you wish to configure.
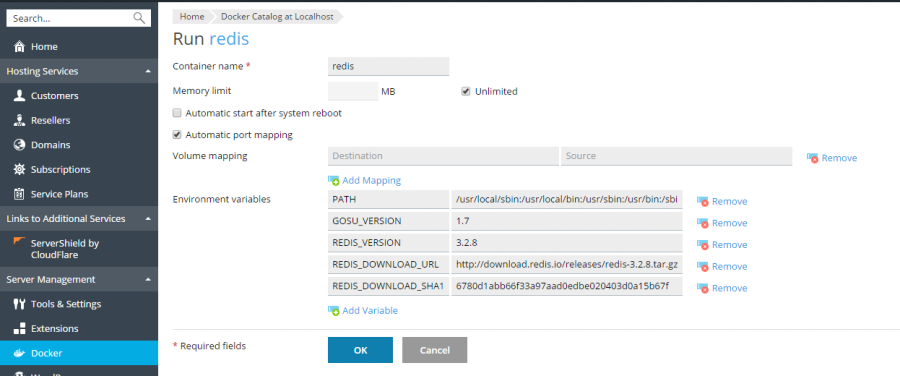
Memory Limits
By default, Docker containers operate with unlimited access to RAM. To impose a limit on memory usage, simply select the Memory limit checkbox and specify the desired maximum value in megabytes within the MB field.
Important: Currently, it is not possible to limit CPU or disk usage for Docker containers directly within Plesk.
Note: Docker containers are considered administrator-level objects and are therefore not subject to subscription-level cgroup limits, which typically control CPU, RAM, and disk usage for individual subscriptions.
Automatic Container Start
For continuous service availability, it is highly recommended to enable the Automatic start after system reboot option. If this option remains unselected, any websites relying on this container may become inaccessible after a system reboot, requiring manual intervention to restart the container.
Port Mapping Configuration
By default, Automatic port mapping is enabled, which means the container’s internal port is automatically mapped to a randomly assigned port on the host system (e.g., 32768).
To customize the host system port, simply deselect Automatic port mapping and enter your desired external port in the Manual mapping field. If the Manual mapping option is not visible after deselecting, it indicates that the container is not designed to expose any ports.
When utilizing manual mapping, Docker, by default, binds the specified port exclusively to the localhost interface (127.0.0.1) of the host system. This configuration ensures that the port remains inaccessible from the internet, thereby enhancing the security of the application running within the container. Should you require the Docker service to bind the specified port to all network interfaces of the host system, deselect the Make the port inaccessible from the Internet option. Be aware that this action will make the application inside the container reachable from the internet via any of the host system's IP addresses on the designated port.
Security Warning: Docker assumes that applications handle their own authentication mechanisms. However, this is not always the case (e.g., MySQL/MariaDB typically requires authentication by default, while Redis may not). Exposing an application inside a container directly to the internet without proper authentication and security configurations can significantly increase its vulnerability to malicious attacks. Exercise caution and ensure robust security measures are in place.
Volume Mapping for Persistent Storage
Docker volumes serve as directories on your server that are mounted directly into a Docker container. This crucial feature provides persistent storage, ensuring that data can be accessed reliably from your host system. Importantly, data stored within Docker volumes is preserved even when a container is stopped or deleted.
Data Backup Warning: Data residing in Docker volumes is explicitly excluded from Plesk's standard backup procedures. To safeguard against potential data loss, it is imperative to implement a third-party backup solution for any critical data stored within these volumes.
For an in-depth understanding of data management in containers, consult the official Docker documentation.
To establish a new volume mapping, you need to specify two absolute paths:
- Host field: Enter the absolute path to the directory on your server that you intend to mount into the container.
- Container field: Provide the absolute path to a directory located inside the container where the host directory will be mounted.
Should you need to map additional directories, simply click the Add one more button.
Configuring Environment Variables
Environment variables play a critical role in configuring applications running within a Docker container. You may find it necessary to add new variables or modify existing ones to tailor the application's behavior. Plesk provides the flexibility to add an unlimited number of environment variables as required by your application.
Essential Container Operations
Plesk offers a comprehensive set of operations for managing your Docker containers effectively:
- You can easily Stop, Start, or Restart any container. It's important to note that performing these actions will cause the container to be recreated using its current settings.
Important Note: If you have not saved your data to mounted volumes (as explained in the "Volume Mapping" section), any unsaved data will be lost upon container recreation.
To monitor container activity, click the arrow icon next to a container to access its logs and observe resource consumption.
Modify container settings by clicking the settings icon
next to a container to access its logs and observe resource consumption.
Modify container settings by clicking the settings icon Further actions can be accessed by clicking the more options icon ![]() next to a container:
next to a container:
- Recreate: Rebuild the container using the same or a different version of the image.
- Save as Image: Create a new image based on the container, including any custom settings you have applied.
- Download Snapshot: Generate and download a snapshot of the container's current state.
- Remove: Delete the container from your system.
Recreating a Docker Container
Recreating a container is typically performed when you need to update the embedded application to a newer version. However, it's worth noting that you have the flexibility to rebuild a container using any available application version from the catalog, not just newer ones.
During the recreation process, all custom settings you have applied to the container will be preserved. To ensure the continuity of data used by the application within the container, it is essential to configure volume mapping prior to recreation. Volume mapping facilitates access to directories utilized inside a container, providing persistent storage as detailed in the "Volume Mapping" section of container settings.
To recreate a container, follow these steps:
- Navigate to Docker and click the more options icon
 situated next to the container you wish to recreate.
situated next to the container you wish to recreate. - Select Recreate from the container settings menu. You will then be prompted to specify the desired image version and whether to utilize default environment variables for the new instance.
Integrating and Using Remote Docker Services
While Plesk defaults to using a locally installed Docker service, the platform also supports integrating and managing Docker services installed on external, remote hosts. It's important to remember that only one Docker service (either local or remote) can be active within Plesk at any given time. The currently active server is clearly indicated in the Environments tab of the Docker settings page.
Important Note: Accessing and managing remote Docker services necessitates a specific Plesk license key add-on. Without this add-on, your capabilities will be limited to controlling only the local Docker service running directly on your Plesk server.
Configuring the Remote Docker Server
To successfully integrate a remote server running Docker with Plesk, you must first configure the remote server itself. This configuration involves setting up secure communication using TLS. Detailed instructions for this setup can be found in the official Docker documentation on securing the Docker daemon with HTTPS.
Connecting and Managing Remote Docker Services
Plesk facilitates the establishment of secure connections between your Plesk server (equipped with the Docker extension) and a remote node running the Docker service. The following detailed steps are applicable for both Linux and Windows Plesk installations.
Steps to perform on the Remote Docker Host:
- Create Docker Configuration File: Create the
/etc/docker/daemon.jsonconfiguration file on your remote server with the following content. This configures Docker to listen for remote connections over TCP with TLS encryption enabled.
{
"hosts": ["tcp://0.0.0.0:2376", "unix:///var/run/docker.sock"],
"tls": true,
"tlsverify": true,
"tlscacert": "/root/ca.pem",
"tlscert": "/root/server-cert.pem",
"tlskey": "/root/server-key.pem"
}
openssl genrsa -aes256 -out ca-key.pem 4096
openssl req -new -x509 -days 365 -key ca-key.pem -sha256 -out ca.pem
openssl genrsa -out server-key.pem 4096
openssl req -subj "/CN=192.0.2.1" -new -key server-key.pem -out server.csr
openssl x509 -req -days 365 -sha256 -in server.csr -CA ca.pem -CAkey ca-key.pem -CAcreateserial -out server-cert.pem
openssl genrsa -out key.pem 4096
openssl req -subj '/CN=client' -new -key key.pem -out client.csr
openssl x509 -req -days 365 -sha256 -in client.csr -CA ca.pem -CAkey ca-key.pem -CAcreateserial -out cert.pem
chmod 0400 ca-key.pem server-key.pem key.pem
chmod 0444 ca.pem server-cert.pem cert.pem
cp /lib/systemd/system/docker.service /etc/systemd/system/
sed -i 's/\ -H\ fd:\/\///g' /etc/systemd/system/docker.service
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl restart docker
.pem files are essential for your Plesk client to establish a secure remote connection.
cat key.pem
cat cert.pem
cat ca.pem
Steps to perform on the Local Plesk Server:
- Navigate to Docker > Environments.
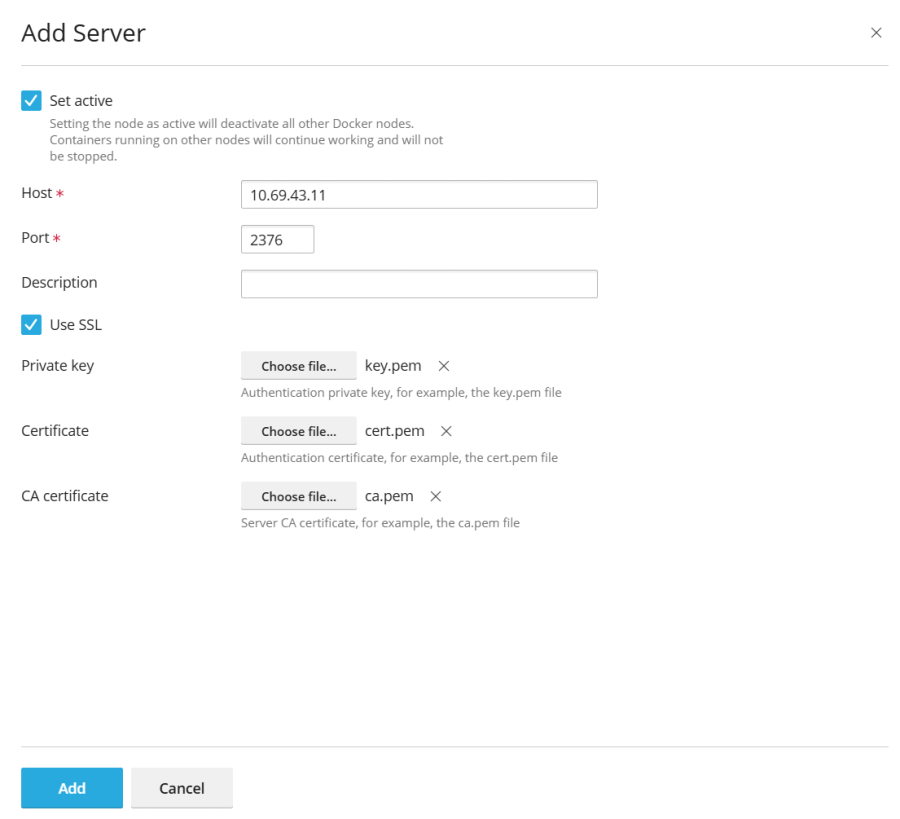
- Click Add Server
 and accurately input the details of your remote Docker server.
and accurately input the details of your remote Docker server. - To immediately activate and begin using this remote Docker service within Plesk, ensure that the Set active option remains selected during configuration.
Once configured, the link to the Docker service will become visible and accessible in the Navigation Pane.
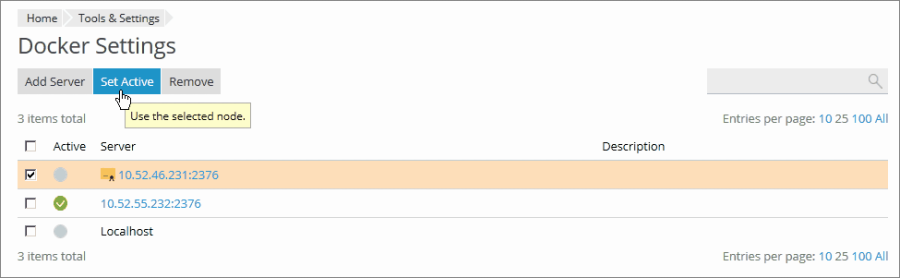
To switch between different Docker services (local or remote):
- Go to Docker > Environments.
- From the displayed list of servers, select the Docker node you wish to use and click Set Active.
Alternatively, you can mark a Docker node as active while you are in the process of editing its settings.
Creating Custom Docker Images from Containers
Should you wish to capture and save the modifications you've made to a running container as a new, reusable image, Plesk provides the convenient Save as Image command. This action effectively takes a snapshot of your container's current state, including any custom configurations, and registers it as a new image within your image catalog. This process is invaluable for creating custom images pre-configured with specific settings, such as tailored environment variables.
To create a new image from an existing container:
- Navigate to Docker > Containers.
- Click the more options icon
 next to the container from which you want to create an image.
next to the container from which you want to create an image. - Select Save as Image.
- In the "Save <container name> as Image" side panel, you will need to specify the following:
- Image name: Provide a descriptive name for your new custom image.
- Tag (Optional): You can specify a version tag for your image. If left blank, the image will be tagged as "latest" by default.
Once created, this new image will appear in the Images tab, clearly marked as a Local image.
Managing Local Docker Images
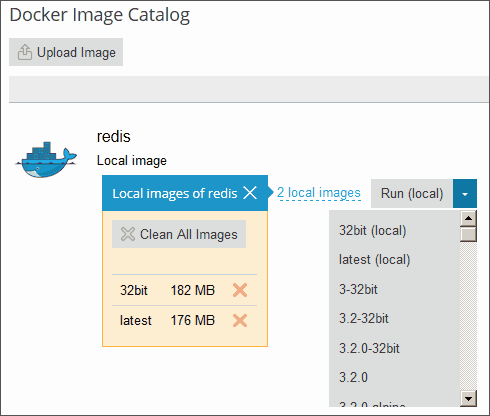
Local Docker images are those that have been downloaded and are stored directly on your server's local disk. This eliminates the need to download them again from the online Image Catalog, significantly speeding up deployment processes.
An image typically becomes a local image under the following circumstances:
- When you select any version (tag) of an image and the download process commences. Even if you later run a container from it or cancel the operation on the "Settings" screen, the image is retained locally.
- You manually upload an image to Docker within Plesk using the Upload image option in the Docker Images tab.
- You create a custom image directly from an existing container, as detailed in the "Creating Custom Docker Images from Containers" section.
- You build an image using the command-line interface.
To download an alternative version of an image from the online catalog, click the Pull icon ![]() . Then, select your desired version from the drop-down menu and click Pull.
. Then, select your desired version from the drop-down menu and click Pull.
If at least one version of an image group is downloaded, that image will be labeled as a Local image in the catalog. Plesk also conveniently displays the total number of local images available for a particular product.

To efficiently manage and remove outdated local images:
- Navigate to Docker > Images.
- Utilize the Search bar to quickly locate a specific local image.
- To view all local images associated with a particular product, click the link beneath the product name. This will display all tags for local images and the disk space they occupy.
- Select the specific image(s) you wish to remove and click the Remove button.
Configuring Nginx to Proxy Requests to Docker Containers
Many Docker containers are designed to expose specific ports, allowing the applications running within them to be accessible. However, when integrating such an application with your website, requiring users to specify a non-standard port in the URL can be inconvenient and less user-friendly.
To circumvent this, you can configure Nginx to act as a reverse proxy, forwarding requests from your domains to the Docker container's designated port. This setup enables your domains to utilize standard web ports (like 80 or 443), eliminating the need for explicit port specification in URLs.
Requirements for Nginx Proxying:
- Nginx must be actively running within your Plesk environment.
- You must manually map the internal port of your Docker container to a specific port on the host system (e.g., 32768).
Steps to Manually Map a Container Port:
- Navigate to Docker > Containers and click the settings icon
 adjacent to the container you intend to configure.
adjacent to the container you intend to configure. - Deactivate the Automatic port mapping option.
- Manually map the container's internal port to a specific, available port on your host system (for instance, 32768). You have the option to make this mapped port inaccessible from the internet for enhanced security.
Once the container port is manually mapped, you can proceed to set up Nginx to proxy requests. This involves adding a proxy rule within your domain's settings in Plesk.
Adding an Nginx Proxy Rule in Domain Settings:
Follow these steps to establish a proxy rule:
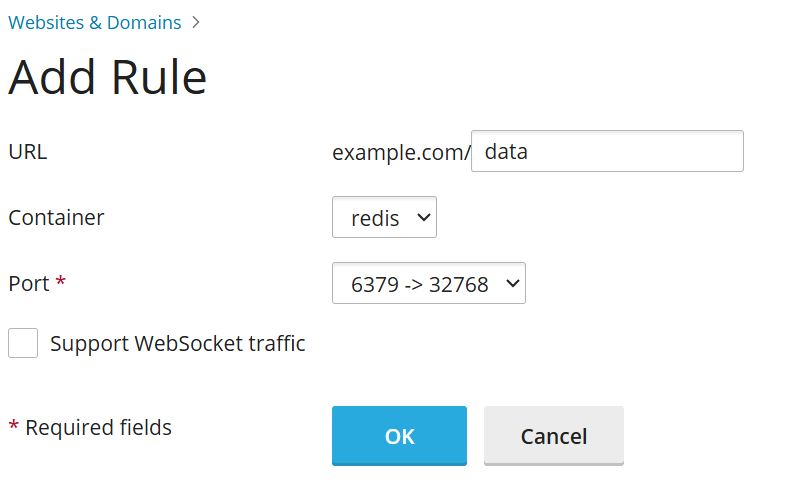
- Go to Websites & Domains, select the relevant domain, then navigate to Docker Proxy Rules, and click Add Rule.
- URL: Specify the URL of the website or a specific section of the website that will utilize the application running in the Docker container.
- Container: Choose the Docker container application you wish to proxy requests to.
- Port: Select one of the port mappings previously configured in the container settings (the host system port to which the container's internal port is mapped). Nginx will then proxy incoming requests to this specific host system port.
These proxy rules are seamlessly integrated into your web server's configuration, typically found in the website’s nginx.conf file (located in /var/www/vhosts/system/$domain/conf/). An example of the generated configuration block is shown below:
#extension docker begin
location ~ ^/.* {
proxy_pass http://0.0.0.0:9080;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
}
#extension docker end
It is important to note that these proxy rules are designed to function correctly even on servers operating behind a Network Address Translation (NAT) setup.
Note on Disk Space Usage: Docker containers linked through Proxy Rules to a website generally do not contribute to the subscription’s reported disk space usage. An exception occurs if a website directory is mounted directly into a Docker container as a volume; in such a scenario, all files within that volume *will* be counted towards the website's disk space allocation.
Deploying Applications with Docker Compose YAML Files
Plesk simplifies the deployment of multi-container Docker applications by supporting Docker Compose YAML files. You have several convenient options for deployment: using an integrated online text editor, uploading a file from your local storage, or selecting a Docker Compose file already present within a website’s Home directory.
Once deployed, Plesk supports typical Docker Compose operations on these application stacks, including up (which encompasses pull and force-recreate), stop, and down. This allows for full lifecycle management, enabling you to modify and update your deployed stacks as needed after their initial creation.
Important Note: This section is specifically for Docker Compose YAML files. It does not support the deployment of Dockerfiles or other supplementary files required by an application.
Steps to Deploy a Docker Compose File:
- Navigate to Docker > Stacks > Add Stack.
- Provide a suitable project name for your application and then select one of the following methods for deploying your Docker Compose file:
- Editor: Directly define or paste the content of your Docker Compose file into the provided text editor.
- Upload: Browse and upload a Docker Compose file from your local computer storage.
- Webspace: Choose a Docker Compose file that is already stored within a domain’s Home directory. If selecting this option, you will first specify the domain where the file is located, then browse to the precise location of the Compose file.
Furthermore, Plesk allows you to declare and build custom containers as part of your Docker Compose setup. Any artifacts generated during this build process will be conveniently stored within the website’s Home directory.
For comprehensive details on the Docker Compose file format and its capabilities, please refer to the official Docker documentation.
Deploying and Managing Portainer with Docker
Portainer is an intuitive and powerful container management software designed to simplify the deployment of individual containers and complex application stacks. It provides a user-friendly interface for monitoring container status and logs, establishing user accounts and teams, securing your Docker environments, and much more.
To install Portainer within your Plesk Docker environment, navigate to Docker > Install Portainer. Once the installation process is successfully completed, you can access and manage your Portainer containers by going to Docker > Go to Portainer.
Please Note: At this time, Portainer integration within Plesk is considered a beta feature.
For detailed information and advanced usage of Portainer, consult the official Portainer documentation.




