The MySQL database server stands as a foundational component for countless content management systems and e-commerce applications globally. It is instrumental in providing the secure and reliable data storage and retrieval capabilities that power dynamic, personalized websites. cPanel & WHM offers a comprehensive MySQL management solution, automating numerous routine web hosting database tasks while granting web hosts the granular control they often require.
While websites and their corresponding cPanel MySQL instances are commonly co-located on the same server, there are distinct advantages to separating them. Utilizing a remote MySQL database, hosted on a distinct server, can significantly enhance performance, security, and scalability for your web applications.
Implementing a remote MySQL server can offer several strategic benefits:
- Offload Database Workloads: By dedicating a separate server to database operations, you can significantly offload processing demands from your webserver. This optimizes resource allocation, leading to improved performance for busy websites and the database itself, ensuring faster query processing and better user experience.
- Specialized Database Hosting: A remote setup allows you to leverage a server specifically configured and optimized for database hosting. Such servers can be equipped with specialized hardware, tuning, and security measures tailored for database performance and resilience, rather than general web serving.
- Centralized Database Management: For environments managing multiple web servers or applications, a centralized remote database simplifies management. It allows for easier administration, backups, and scaling of your database infrastructure across various sites from a single point.
- Enhanced Security and Isolation: Isolating your database on a separate server, distinct from those directly exposed to public IP addresses, significantly enhances security. This creates an additional layer of defense, making it harder for potential attackers to gain direct access to your sensitive data, even if the webserver is compromised.
It is crucial to understand that exposing your MySQL server directly to the public internet and permitting connections from untrusted IP addresses is an insecure practice. This approach creates a critical security vulnerability that malicious actors frequently exploit to compromise data integrity or steal sensitive information.
This article will guide you through the correct and secure method for configuring MySQL to accept connections from web applications hosted on different servers, leveraging cPanel's robust management features.
Using a Remote Database to Host Your Site’s Data
To successfully follow this comprehensive tutorial, please ensure you have the following prerequisites:
- Remote Database Server: A dedicated server with cPanel & WHM properly installed. This server will function as your remote MySQL database host.
- Access Credentials: The IP address or domain name of your database server, along with valid cPanel authentication credentials, and the necessary MySQL username and password for database access.
- Web Application Server: A separate server where your web applications will be installed. While manual site installation and configuration are feasible, using cPanel on this server can significantly streamline the setup process, offering greater speed and convenience.
We will begin by explaining how individual cPanel users can configure access to a remote MySQL database, followed by an exploration of WHM's advanced MySQL Profile management tools for system administrators.
Configuring a Remote MySQL Database with cPanel
To begin, log in to your cPanel account on the server hosting the MySQL instance you intend to grant remote access to. From the main cPanel dashboard, locate and select the Remote MySQL® tool. This utility allows you to specify which external hosts are permitted to connect to your databases.
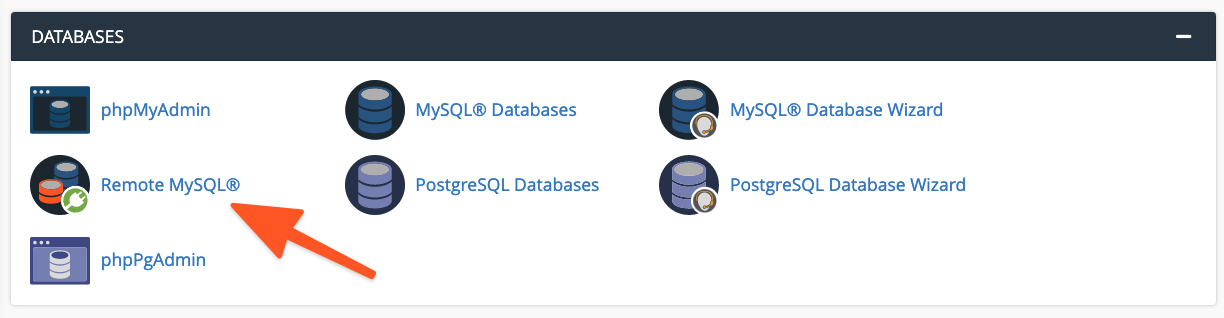
Within the Add Access Host form, you will need to input the domain name or IP address of the server where your web application is hosted. For scenarios requiring access from a range of IP addresses, you can employ a wildcard character (%). For instance, entering 192.68.0.% would permit connections from any IP address within the 192.68.0.x subnet. When utilizing wildcards, it is imperative to exercise caution and restrict the scope to IP addresses that are under your direct control or that you are absolutely confident pose no security risk. Overly broad wildcards can expose your database to unnecessary vulnerabilities.
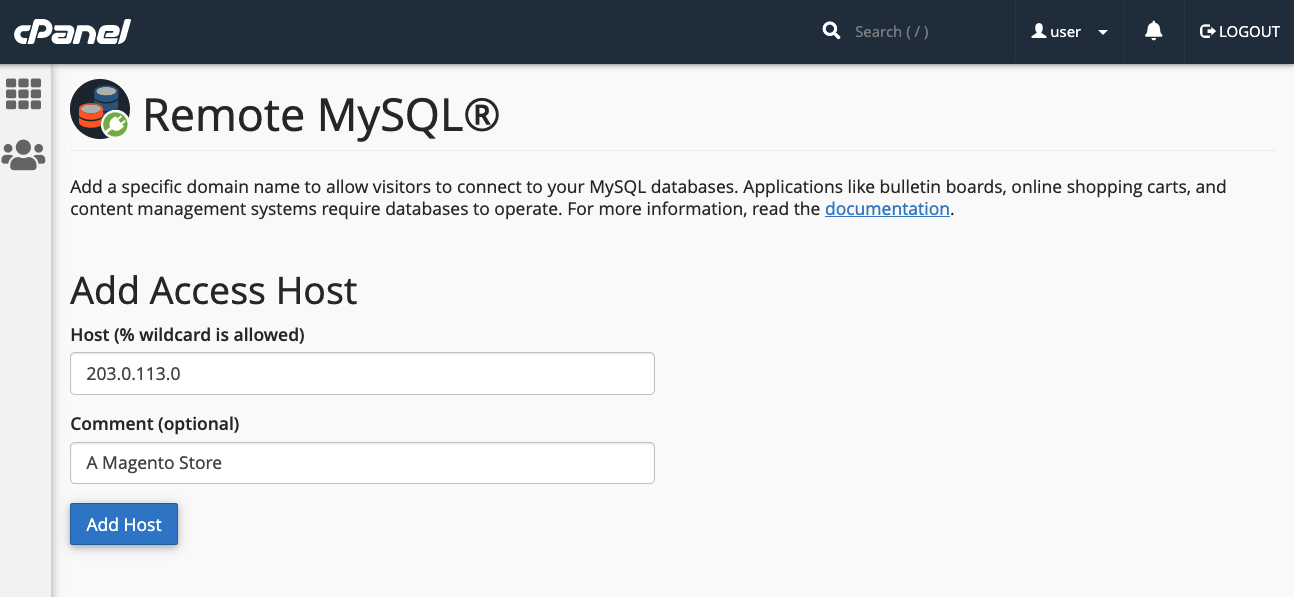
After entering the host information, click the Add Host button. cPanel will then automatically configure the MySQL database to accept incoming requests from the specified remote server, establishing the necessary connection permissions.
The subsequent step involves configuring your web application to utilize this newly accessible remote database. The exact procedure for this configuration varies depending on the specific application you are using. For example, when setting up a new WordPress site, you would first create the database using cPanel’s MySQL® Database Wizard.
Following database creation, you would then edit the wp-config.php file of your WordPress installation. This file requires updates to include the database name, authentication credentials (username and password), and crucially, the domain name or IP address of your remote MySQL server. An example configuration might look like this:
define( 'DB_NAME', 'wp_database' );
define( 'DB_USER', 'user' );
define( 'DB_PASSWORD', 'a-secure-password' );
define( 'DB_HOST', '203.0.113.0' );
Adding MySQL Access Hosts in WHM
For system administrators, WHM provides a centralized method to configure MySQL for accepting incoming connections from remotely hosted websites. It's important to note key distinctions between configuring access through cPanel and WHM:
- Global Application: Hosts added via WHM are applied universally to all cPanel user accounts and their associated MySQL users on that server. This offers a broad, server-wide configuration.
- Persistent Configuration: Once a host is added by a system administrator in WHM, individual cPanel users do not have the ability to permanently remove these entries, ensuring consistent access control.
To grant remote hosts access to your MySQL databases at the WHM level, navigate to the SQL Services section in the sidebar menu, then select Additional MySQL Access Hosts.
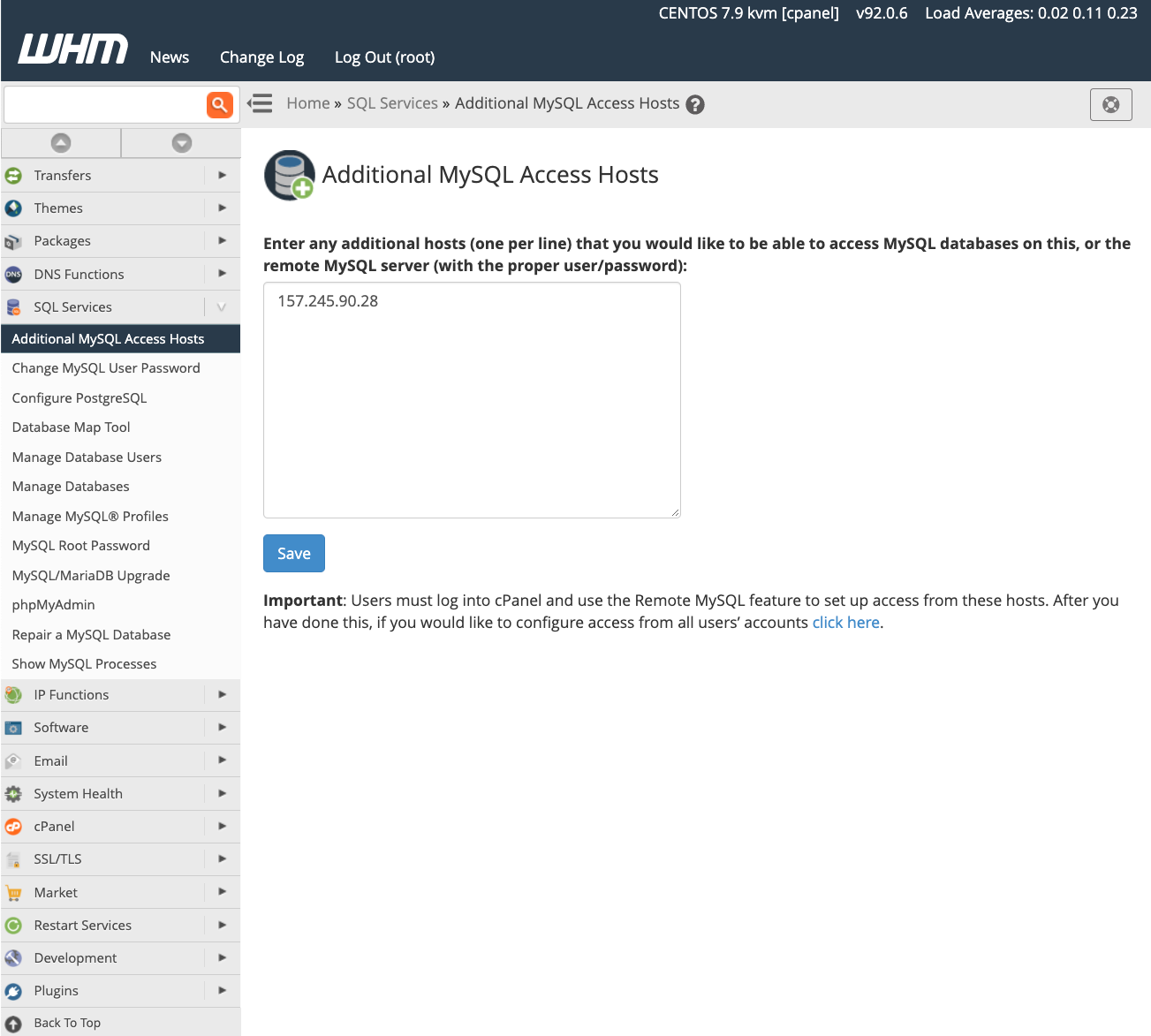
In the provided interface, enter the domain names or IP addresses of all remote hosts that require permission to connect to the server’s MySQL databases. After entering the necessary information, click Save. Following this, you must configure your web applications with the appropriate database server IP address and authentication credentials, as detailed in the preceding section, to establish connectivity.
For a deeper dive into the functionalities and best practices for managing database access hosts, we recommend consulting the official feature documentation page.
Managing MySQL Profiles in WHM
Beyond individual host access configuration, WHM offers server administrators the advanced capability to create and manage MySQL profiles. These profiles are instrumental in defining the remote database server that cPanel & WHM will utilize for all its database operations. Even the local machine’s default MySQL instance is managed through an active profile.
MySQL profiles are versatile and can be configured to connect with various types of remote database solutions. This includes databases running on other cPanel & WHM servers, dedicated MySQL database servers, or even managed database services like Amazon’s Relational Database Service (RDS).
It is important to note a critical limitation: only one MySQL profile can be active at any given time. Before proceeding to create and activate a new profile, ensure you understand its implications. To add a new profile, log in to WHM and navigate to Manage MySQL® Profiles, located under the SQL Services section in the sidebar menu.
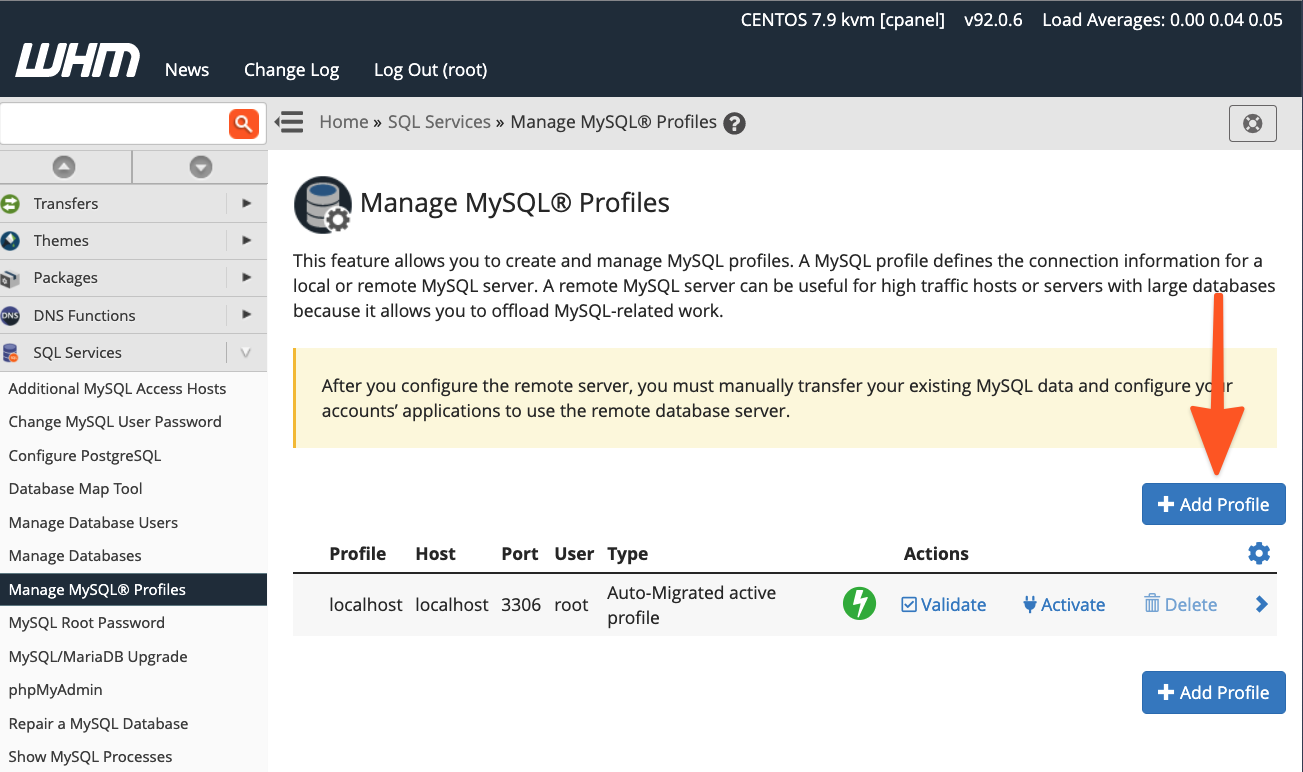
WHM provides a streamlined process for profile creation. It can automatically log into the specified remote server, establish a new MySQL superuser account for database management, and configure the MySQL instance accordingly. Alternatively, if you have already set up the MySQL installation with a dedicated superuser, you have the option to input those existing credentials instead.
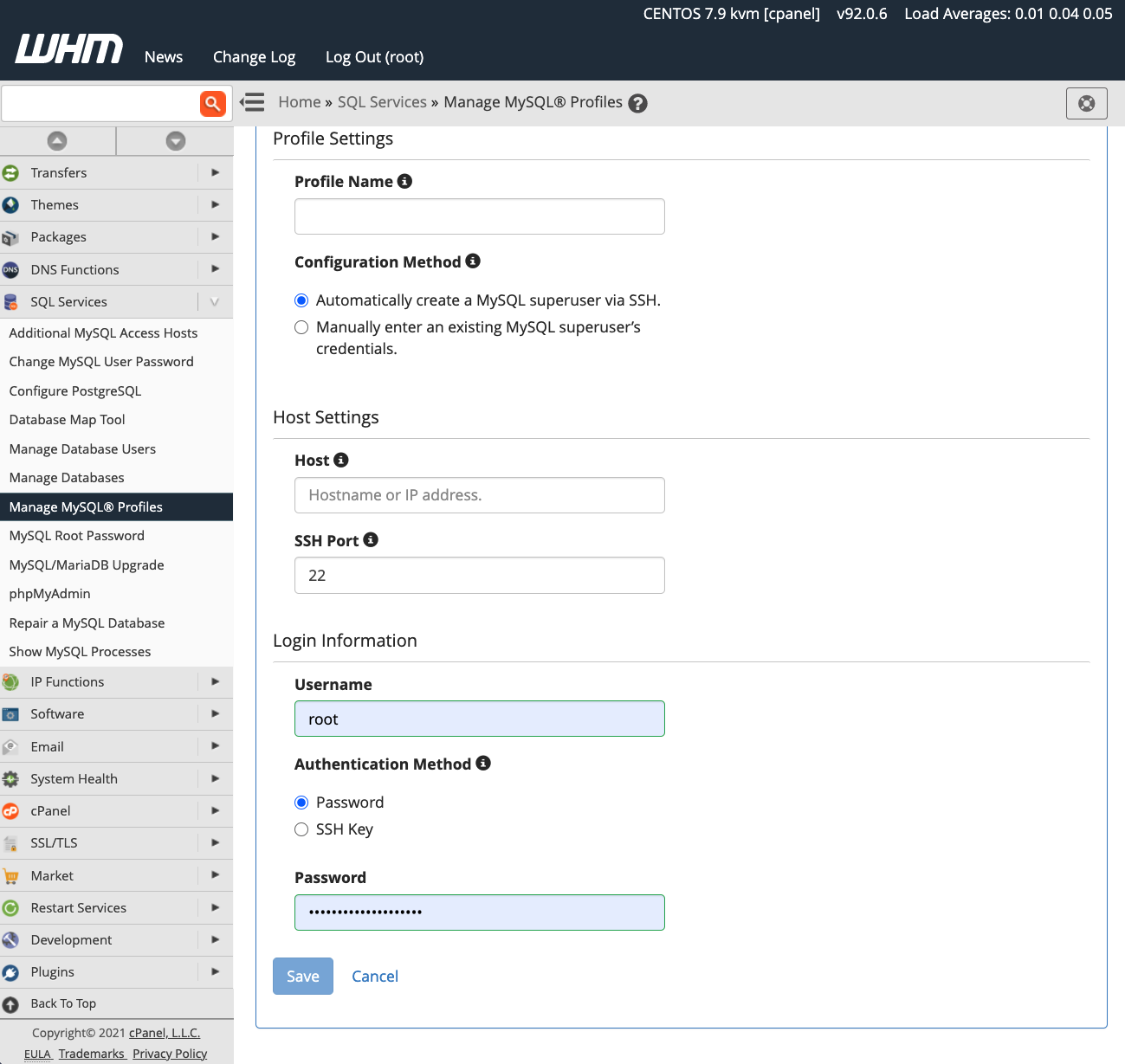
Once your new MySQL profile is activated, all subsequent database creations will occur on the designated remote server. However, it's crucial to understand that existing databases are not automatically migrated to the new remote profile. Any data from existing local databases will need to be manually transferred to the remote server to ensure continuity.
In summary, cPanel & WHM empowers web hosts and their clients with exceptional flexibility in configuring and managing MySQL databases, offering a range of powerful capabilities:
- Optimal Local Hosting: Provides outstanding, ready-to-use defaults for hosting MySQL databases directly on the local server, simplifying initial setups.
- Seamless Remote Configuration: Facilitates easy and secure database configuration for websites and e-commerce stores hosted on separate, remote servers.
- Comprehensive Administrative Control: Offers advanced system administrator tools that provide complete command over MySQL installations and precise control over where databases are hosted, whether locally or remotely.




