To ensure your server efficiently executes scripts at predetermined times, Plesk Obsidian provides a robust task scheduler facility. This feature, often referred to as cron jobs on Linux systems, allows the system to run specified scripts automatically, streamlining various administrative and operational processes, from routine backups to script executions and automated updates.
Managing Existing Scheduled Tasks in Plesk
For a comprehensive overview of all scheduled tasks, whether created at the server level or for individual subscriptions, navigate to Tools & Settings > Scheduled Tasks (Cron jobs). This central location offers a clear dashboard of all automated operations running on your server.
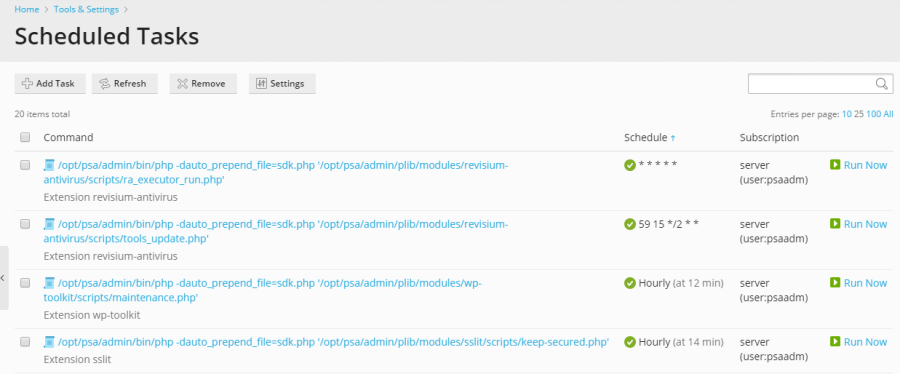
The interface allows you to easily sort tasks by command, associated subscription, or schedule. Sorting by schedule can be particularly valuable for identifying and troubleshooting potential server load issues that may be caused by resource-intensive tasks executing concurrently at certain times. For each task listed, you have the flexibility to adjust its properties by clicking on its name, activate it using the  icon, deactivate it via the
icon, deactivate it via the  icon, or even initiate an immediate run for testing purposes or urgent execution.
icon, or even initiate an immediate run for testing purposes or urgent execution.
Important Considerations for Linux Environments
Note: In Plesk for Linux, scheduled tasks created by Plesk users are executed within a chrooted shell by default. This security measure changes the file system root to the corresponding system user’s home directory, significantly enhancing server security by restricting access to other parts of the file system. While beneficial for overall security, it is important to note that this setup may limit some specific options for Plesk users. The shell used for scheduled tasks for all Plesk users can be modified by going to Tools & Settings > Scheduled Tasks > Settings. For more in-depth information about shell settings and their implications, please refer to the Scheduled tasks shell setting documentation.
Creating New Scheduled Tasks
To set up a new automated task tailored to your specific needs, proceed to Tools & Settings > Scheduled Tasks > Add Task. The initial step involves selecting the appropriate task type, which dictates how the system will execute your command or script on the server.
Understanding Task Types
- Run a command: This option is used for executing binary files, custom shell scripts, or batch files directly on the server. You must specify the full, absolute path to the executable file, ensuring the system can locate and run it correctly within the designated environment.
- Fetch a URL: Ideal for triggering web-based actions, external cron jobs, or API calls. Simply provide the complete URL; Plesk automatically handles the underlying command execution (such as using
curlorwgetin the background), eliminating the need for manual command typing. - Run a PHP script: Specifically designed for executing PHP scripts. Provide the full path to your script, for instance,
/tmp/script.php. This ensures the script is run with the correct PHP interpreter and the appropriate environment variables.
Configuring Task Schedule and Properties
Once the task type is selected, you will define its execution frequency and specify the exact time and date for its operation. By default, the task will operate according to the server's time zone. Should you require a different time zone for your tasks to align with specific operational requirements, this can be configured under Tools & Settings > Scheduled Tasks > Settings. Additionally, you have the ability to add a clear and concise descriptive label for the task, select the specific system user under whose security context the task will run (a crucial step for managing file permissions and access), and configure notification preferences to stay informed about task execution status, including any potential errors.
Testing Your Scheduled Tasks
Before finalizing and saving your new scheduled task, it is highly recommended to perform a test run. Click the Run Now button and observe the task's completion and output. This pre-check allows you to verify that the task is configured correctly and functions as expected without errors. If the test run concludes with an error, it is imperative to identify and resolve the underlying issue before relying on the scheduler, as the task will similarly fail during automated execution, potentially disrupting your operations. This step is vital for ensuring reliability.




